In the rapidly evolving landscape of modern healthcare, technology plays a pivotal role in enhancing efficiency, improving patient outcomes, and streamlining clinical workflows. Among the most impactful innovations are medical touch screen displays, which have transformed how medical professionals interact with critical data, imaging, and equipment. These specialized displays are not merely consumer-grade touchscreens adapted for medical use; they are purpose-built devices engineered to meet the stringent demands of clinical environments, prioritizing precision, hygiene, and unwavering reliability. From operating rooms and intensive care units to diagnostic imaging centers and patient registration desks, medical touch screen displays are becoming indispensable tools, offering intuitive interfaces and robust performance that directly impact patient safety and operational effectiveness.
The Critical Importance of Specialized Medical Touch Screens in Healthcare Environments
The unique challenges of healthcare settings necessitate display solutions far beyond the capabilities of standard commercial screens. Medical environments are characterized by strict sanitation protocols, the presence of electromagnetic interference from other medical devices, and the need for absolute accuracy in data presentation. This section explores why specialized medical touch screen displays are not just an advantage but a necessity.
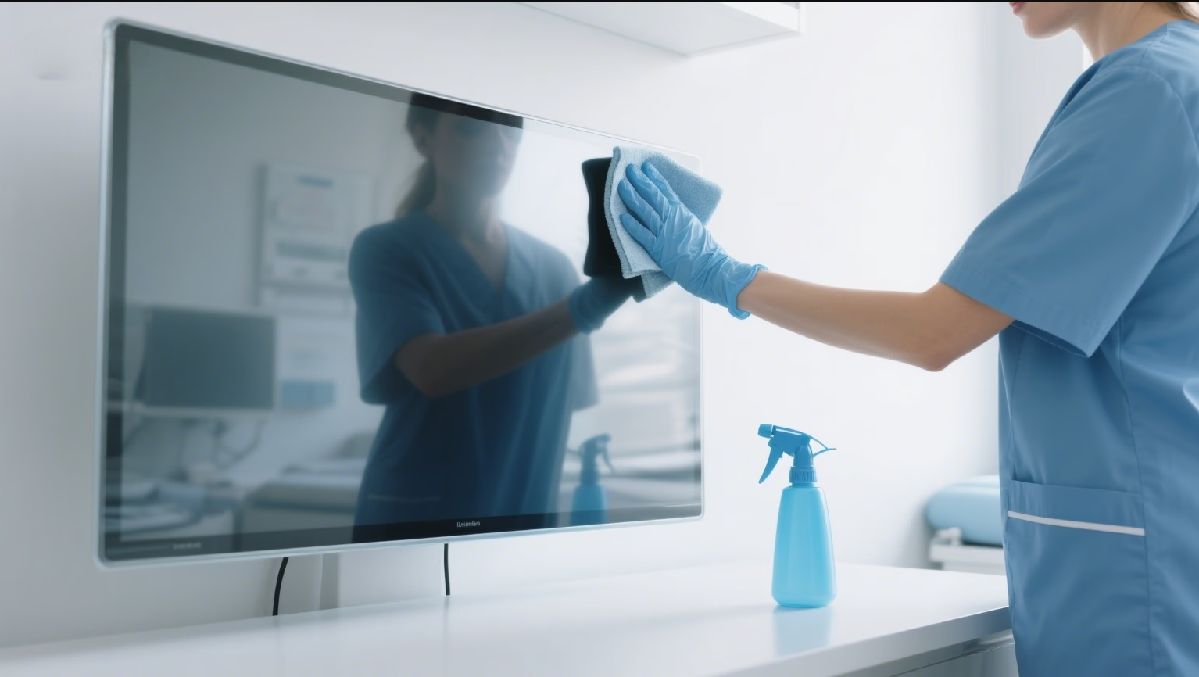

Uncompromising Hygiene and Infection Control: A Top Priority
One of the foremost considerations in any medical setting is infection control. Medical-grade touch screen displays are specifically designed to facilitate rigorous cleaning and sterilization procedures, crucial for preventing the spread of hospital-acquired infections (HAIs). Unlike conventional displays with intricate bezels and fan vents that can harbor pathogens, medical touch screens often feature:
- Flat, Bezel-Free Surfaces: These designs eliminate crevices where bacteria can accumulate, making them easier to wipe down thoroughly.
- IP-Rated Enclosures: Ingress Protection (IP) ratings, such as IP65 or higher, indicate resistance to liquids and dust, allowing for frequent cleaning with disinfectants without damaging internal components. This is especially vital for waterproof medical displays used in sterile environments or near sinks.
- Antimicrobial Coatings: Some advanced displays incorporate antimicrobial surface treatments that actively inhibit the growth of bacteria, fungi, and viruses, adding an extra layer of protection.
The ability to maintain a sterile environment without compromising functionality is paramount. Healthcare professionals must be able to disinfect equipment rapidly and effectively between uses, ensuring patient safety and adherence to strict regulatory guidelines.
Summary: The design of medical touch screens prioritizes infection control through features like flat surfaces, high IP ratings, and antimicrobial coatings, enabling thorough and frequent disinfection essential for patient safety.
Precision and Clarity: Beyond Standard Visuals
Accuracy in visual information is non-negotiable in medicine. From reading diagnostic images to monitoring vital signs, even subtle inaccuracies can have significant consequences. Medical touch screen displays are engineered to deliver superior visual performance, critical for clinical decision-making.
- High Resolution and Pixel Density: These displays offer sharp, detailed images, crucial for interpreting X-rays, MRI scans, and microscopic views. Higher pixel density ensures that fine details are visible without pixilation, a key feature for high-resolution medical monitors.
- Consistent Brightness and Contrast Ratios: Maintaining uniform brightness across the screen and high contrast ratios allows medical professionals to discern subtle variations in images, which can be indicative of critical conditions.
- Wide Viewing Angles: In a busy clinical environment, multiple professionals may need to view a screen simultaneously. Wide viewing angles ensure that color and image quality remain consistent regardless of the observer’s position, facilitating collaborative care.
- Color Calibration and Consistency: For applications like pathology or surgical visualization, accurate color representation is vital. Medical displays are often factory-calibrated to specific color standards (e.g., DICOM Part 14 for grayscale medical imaging) to ensure consistent and reliable image interpretation across different devices and locations.
The emphasis on precision and visual fidelity means that medical professionals can trust the information presented on these screens, leading to more accurate diagnoses and effective treatment plans.
Summary: Medical touch screens provide unparalleled visual precision through high resolution, consistent brightness, wide viewing angles, and accurate color calibration, ensuring reliable data interpretation for critical medical decisions.
Durability and Reliability in Demanding Environments
Medical equipment operates continuously, often under significant stress and in unpredictable conditions. Unlike consumer electronics, medical touch screen displays are built to withstand the rigors of a 24/7 operational cycle, frequent physical interaction, and potential exposure to various substances.
- Robust Construction Materials: These displays utilize industrial-grade components and ruggedized enclosures made from durable materials like aluminum or medical-grade plastics, resistant to impacts, vibrations, and corrosive cleaning agents.
- Long Operational Lifespan: Engineered for extended use, medical displays are designed to have a significantly longer lifespan than commercial alternatives, reducing replacement costs and downtime.
- Fanless Designs: Many medical touch screens are fanless to prevent the circulation of airborne contaminants and reduce noise in quiet clinical settings. This also eliminates a common point of failure found in fan-cooled devices. This is a key advantage for fanless medical panel PCs.
- Resistance to EMI/RFI: Medical devices generate electromagnetic interference. Specialized shielding ensures that medical touch screens operate without disruption from other critical equipment, maintaining data integrity and system stability. Compliance with medical safety standards (e.g., IEC 60601-1) is a testament to their reliability in these environments.
The inherent durability and reliability of these displays ensure uninterrupted functionality, which is paramount in critical care situations where system failure can have severe consequences.
Summary: Built for resilience, medical touch screens boast robust construction, long operational lifespans, fanless designs, and EMI/RFI resistance, guaranteeing reliable performance in demanding, continuous-operation healthcare settings.
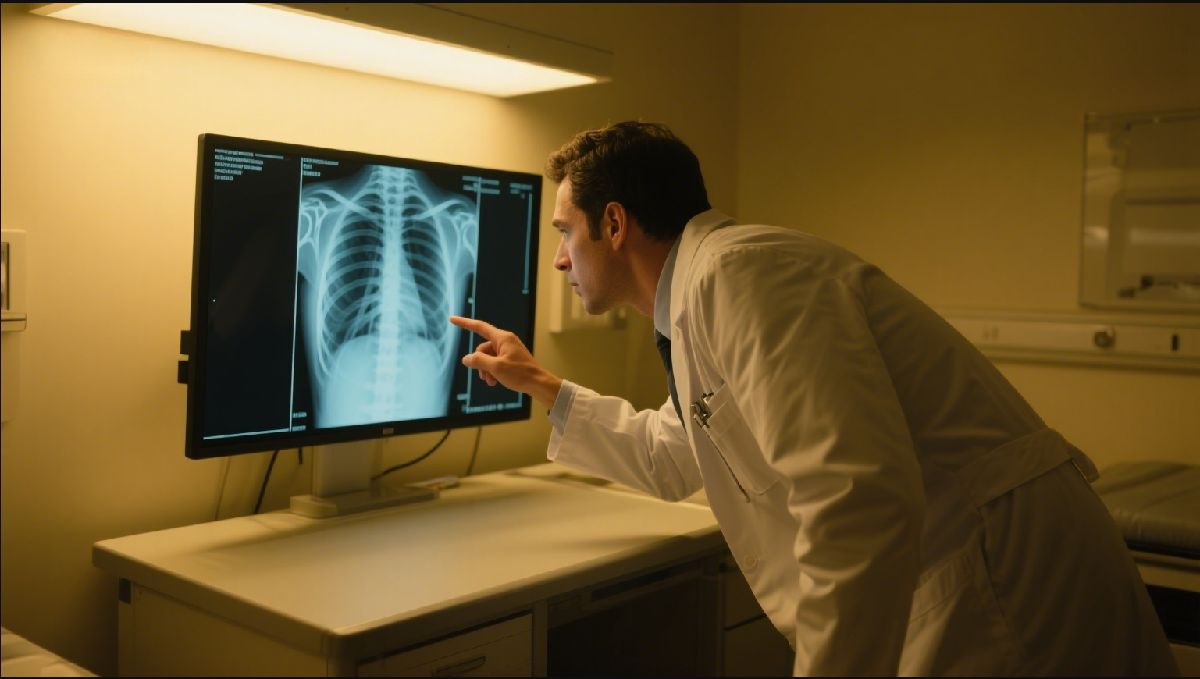
Applications of Medical Touch Screen Displays Across Healthcare Sectors
The versatility of medical touch screen displays allows for their integration into a wide array of healthcare applications, each benefiting from their specialized features. From enhancing direct patient care to streamlining administrative tasks, these displays are transforming operations across the entire spectrum of medical services.
Clinical and Surgical Environments: Precision and Intuition
In operating rooms, intensive care units (ICUs), and emergency departments, every second counts, and every piece of information must be presented clearly and precisely. Surgical touch screen monitors are designed to meet these exact demands.
- Operating Rooms (ORs): Surgeons and anesthesiologists rely on these displays for viewing patient vitals, endoscopic imaging, PACS (Picture Archiving and Communication System) images, and surgical navigation data. The intuitive touch interface allows for quick adjustments and access to critical information without breaking sterility or diverting focus. Features like multi-touch capabilities and glove-friendly screens are invaluable.
- Intensive Care Units (ICUs): In critical care settings, touch screens are used for continuous patient monitoring, displaying real-time physiological data, medication schedules, and historical trends. The ability to quickly zoom in on anomalies or access patient records directly at the bedside enhances rapid response capabilities.
- Diagnostic Imaging: Radiologists and technicians utilize medical imaging displays for detailed analysis of X-rays, CT scans, MRIs, and ultrasounds. These displays adhere to standards like DICOM Part 14, ensuring grayscale consistency for accurate diagnosis.
- Telemedicine and Remote Consultation: High-resolution touch screens with integrated cameras and microphones facilitate remote consultations, allowing specialists to interact with patients and colleagues from a distance, extending healthcare access.
The seamless integration and user-friendly nature of medical touch screens contribute significantly to improved clinical workflows and better patient outcomes in these high-stakes environments.
Summary: Medical touch screens are indispensable in clinical and surgical settings, providing precise, intuitive interfaces for critical data, imaging, and patient monitoring, significantly improving workflows and outcomes in ORs, ICUs, and diagnostic centers.
Patient Engagement and Information Systems: Empowering Individuals
Beyond clinical use, medical touch screen displays are increasingly being deployed to enhance the patient experience, providing interactive access to information and entertainment.
- Interactive Patient Whiteboards: In patient rooms, large touch screens can replace traditional whiteboards, displaying personalized patient information, care team details, daily schedules, and educational content. Patients can interact with these screens to access health information, order meals, or communicate with nurses.
- Patient Check-in Kiosks: At reception areas, touch screen kiosks streamline the check-in process, allowing patients to confirm appointments, update personal information, and even make payments, reducing wait times and administrative burden. These are prime examples of healthcare kiosk solutions.
- Wayfinding Systems: Large, interactive touch screen directories help patients and visitors navigate complex hospital layouts, reducing stress and improving efficiency.
- Digital Signage and Education: In waiting rooms and common areas, touch screens can display health tips, hospital services, and important announcements, engaging patients and providing valuable information.
By empowering patients with accessible information and interactive tools, medical touch screens foster a more engaged and informed patient population, leading to better adherence to treatment plans and overall satisfaction.
Summary: Medical touch screens enhance patient engagement through interactive whiteboards, self-check-in kiosks, wayfinding systems, and digital signage, providing accessible information and streamlining administrative processes for a better patient experience.
Administrative and Laboratory Applications: Streamlining Operations
The utility of medical touch screen displays extends to the operational backbone of healthcare facilities, improving efficiency in administrative tasks and laboratory operations.
- Electronic Health Records (EHR) Access: Clinicians and administrative staff use touch screen displays for quick and secure access to patient EHRs, allowing for efficient data entry, retrieval, and analysis at various points of care. This often involves medical all-in-one PCs for a compact solution.
- Pharmacy and Laboratory Management: In pharmacies, touch screens can be used for dispensing medications and managing inventory. In laboratories, they facilitate sample tracking, test result viewing, and equipment control, ensuring accuracy and efficiency in critical processes.
- Asset Tracking and Inventory Management: Touch screen interfaces on mobile carts or wall-mounted displays can be used to track medical equipment, supplies, and medications, optimizing inventory levels and reducing waste.
- Training and Simulation: Medical schools and training centers utilize touch screen displays in simulation labs for hands-on training, allowing students to interact with virtual patients and practice procedures in a safe, controlled environment.
By digitizing and streamlining these vital administrative and laboratory functions, medical touch screen displays contribute to more efficient operations, reduced errors, and optimized resource allocation across the healthcare system.
Summary: Medical touch screens streamline administrative and laboratory functions, providing efficient access to EHRs, facilitating pharmacy and lab management, enabling asset tracking, and supporting medical training, ultimately boosting operational efficiency and accuracy.
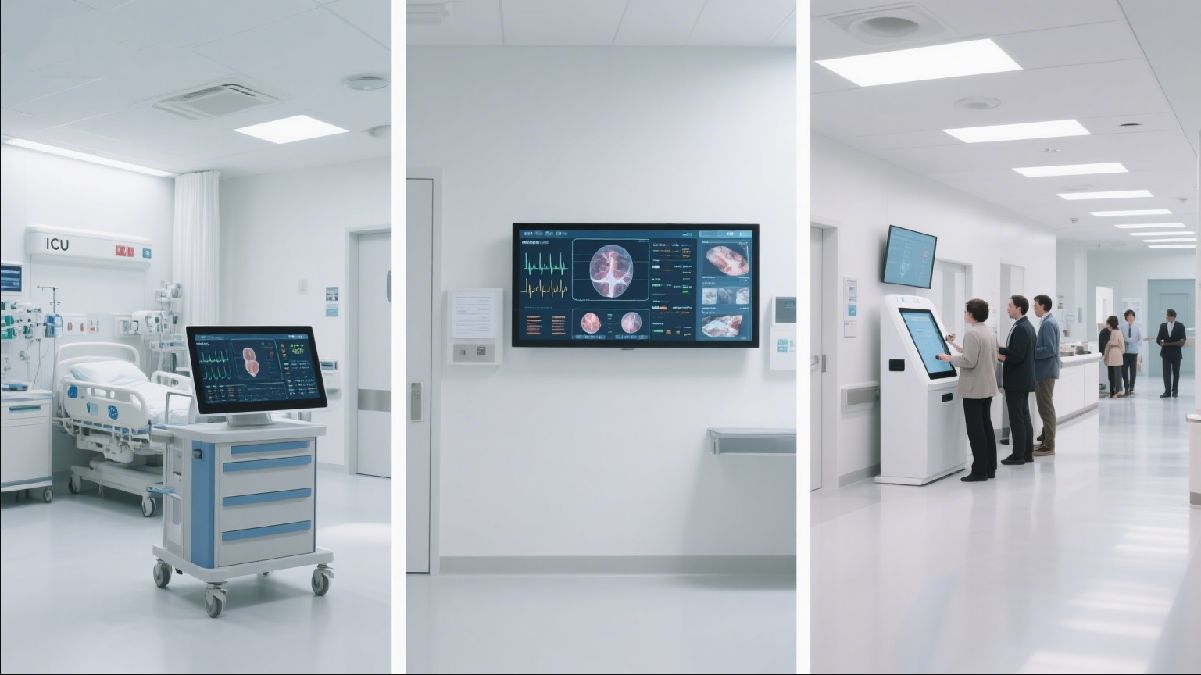
Key Considerations When Selecting Medical Touch Screen Displays
Choosing the right medical touch screen display involves careful consideration of several critical factors. Beyond the basic functionality, healthcare providers must evaluate specifications related to safety, performance, and long-term viability to ensure the chosen solution meets their specific needs and adheres to industry standards.
Compliance with Medical Certifications and Standards
One of the most crucial aspects is ensuring the display complies with relevant medical safety and electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) standards. These certifications are a testament to the display’s design for safe and reliable operation in a clinical environment.
- IEC 60601-1 (Medical Electrical Equipment – Part 1: General Requirements for Basic Safety and Essential Performance): This is the fundamental standard for medical electrical equipment. Displays adhering to this standard minimize risks to patients and operators, including electrical shock, mechanical hazards, and excessive temperature.
- IEC 60601-1-2 (Electromagnetic Disturbances – Requirements and Tests): This part of the standard addresses electromagnetic compatibility, ensuring the display does not interfere with other medical devices and is not unduly affected by their emissions.
- DICOM Part 14 (Grayscale Standard Display Function): For medical imaging displays, adherence to DICOM Part 14 ensures consistent and accurate grayscale rendering, critical for diagnostic interpretation of X-rays, CT scans, and MRIs.
- UL/CE/FCC Certifications: These regional certifications indicate compliance with electrical safety and electromagnetic emission standards relevant to North America, Europe, and other markets.
Verifying these certifications is not just a matter of compliance; it is a critical step in ensuring patient safety and the integrity of medical data.
Summary: Compliance with medical certifications like IEC 60601-1 (safety), IEC 60601-1-2 (EMC), and DICOM Part 14 (imaging) is paramount when selecting medical touch screens, guaranteeing safety and reliable performance.
Display Technology and Touch Technology
The choice of display and touch technology impacts visual quality, responsiveness, and durability.
- Display Technologies:
- IPS (In-Plane Switching) Panels: Offer superior color accuracy and wide viewing angles, making them ideal for collaborative viewing and applications where color fidelity is critical.
- VA (Vertical Alignment) Panels: Provide high contrast ratios and deep blacks, suitable for applications requiring high image depth.
- TN (Twisted Nematic) Panels: Generally less expensive with faster response times, but with narrower viewing angles and less accurate color reproduction. Less common in medical applications where visual precision is key.
- Touch Technologies:
- Projected Capacitive (PCap): The most common and preferred touch technology for medical displays due to its durability, multi-touch capabilities, and sensitivity. It allows for precise input even with gloved hands and supports gestures like pinch-to-zoom. These are often described as multi-touch medical displays.
- Resistive: While less common in new medical displays, resistive touch screens can be activated by any object (gloved hand, stylus) and are highly durable, but typically offer lower optical clarity and no multi-touch.
- Surface Acoustic Wave (SAW): Offers good optical clarity but can be affected by surface contaminants and does not support gloved operation well.
The optimal combination of display and touch technology depends on the specific application and user interaction requirements.
Summary: The selection of display (IPS for color accuracy, VA for contrast) and touch (PCap for durability and multi-touch) technologies is crucial, directly impacting visual quality, responsiveness, and suitability for specific medical applications.
Connectivity and Integration Capabilities
Seamless integration into existing hospital IT infrastructure and compatibility with various medical devices are vital for efficient operation.
- Standard and Medical-Specific Ports: Look for a range of connectivity options, including HDMI, DisplayPort, DVI for video, USB for touch and peripherals, and specialized medical ports like COM ports for legacy medical equipment.
- Network Connectivity (Ethernet/Wi-Fi): Essential for accessing EHR systems, PACS, and other network resources. Secure and stable network connections are critical for data transfer and system updates.
- Power over Ethernet (PoE): For certain applications, PoE can simplify installation by delivering both power and data over a single Ethernet cable, reducing cable clutter and installation complexity.
- Compatibility with Mounting Solutions: Medical displays often need to be mounted on carts, walls, or surgical booms. VESA mount compatibility is essential for flexible deployment.
Future-proofing also involves considering modular designs and upgrade paths that allow for technological advancements without requiring complete system overhauls.
Summary: Robust connectivity (HDMI, DisplayPort, USB, Ethernet) and compatibility with medical-specific ports and mounting solutions are essential for seamless integration into hospital infrastructure and efficient data transfer.
Customization and Serviceability
Healthcare environments often require highly specialized solutions. The ability to customize displays and ensure ease of service are important considerations.
- Customization Options: This can include custom screen sizes, specific housing materials, integrated peripherals (e.g., RFID readers, barcode scanners), and custom branding. For some facilities, OEM medical displays offer tailored solutions.
- Long-Term Availability and Support: Medical equipment typically has a long lifecycle. Choose a manufacturer that offers long-term product availability, reliable technical support, and accessible spare parts to ensure continuous operation and minimize downtime.
- Ease of Maintenance and Repair: Displays that are easy to clean, have readily accessible components for repair, or offer modular designs simplify maintenance and extend the lifespan of the equipment.
Investing in a solution that offers flexibility and reliable support ensures that the medical touch screen displays remain effective and operational throughout their service life.
Summary: Customization options, long-term product availability, robust support, and ease of maintenance are vital for medical touch screens, ensuring tailored solutions and sustained operational efficiency throughout their lifecycle.

The Future of Medical Touch Screen Displays: Innovation and Integration
The trajectory of medical touch screen display technology points towards even greater integration, intelligence, and user-centric design. As healthcare continues its digital transformation, these displays will become even more sophisticated, offering enhanced functionalities that further empower medical professionals and improve patient care.
- Advanced AI and Machine Learning Integration: Future medical displays may incorporate AI directly at the edge, assisting with real-time diagnostic support, predictive analytics for patient deterioration, and intelligent workflow optimization. Imagine a display that highlights anomalies on an X-ray or suggests relevant patient history based on current vitals.
- Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR) Capabilities: The integration of AR/VR elements will revolutionize surgical planning, medical training, and patient education. Surgeons could overlay 3D anatomical models onto real-time patient data, while patients could visualize their treatment plans in an immersive environment.
- Enhanced Haptics and Force Feedback: Beyond visual and auditory cues, future touch screens could provide haptic feedback, simulating textures or resistance, which would be particularly useful in training simulations or for nuanced diagnostic palpation.
- Seamless Interoperability: The emphasis will continue to be on creating displays that effortlessly communicate with a vast ecosystem of medical devices, EHR systems, and cloud-based platforms, leading to truly connected healthcare environments.
- Sustainable and Energy-Efficient Designs: As environmental concerns grow, manufacturers will increasingly focus on developing medical displays that are energy-efficient, made from recyclable materials, and have minimal environmental impact throughout their lifecycle.
The evolution of medical touch screen displays is intrinsically linked to the broader advancements in healthcare technology. These devices will continue to be at the forefront of innovation, driving efficiency, enhancing diagnostic accuracy, and ultimately contributing to a healthier future for all.
Summary: The future of medical touch screen displays involves deeper integration of AI/ML, AR/VR, enhanced haptics, seamless interoperability, and sustainable designs, collectively driving greater efficiency, diagnostic accuracy, and patient care in healthcare.

Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about Medical Touch Screen Displays
Q1: What makes a medical touch screen display different from a regular commercial touchscreen?
A1: Medical touch screens are purpose-built for healthcare environments. Key differences include: * Hygiene: Flat, bezel-free surfaces, high IP ratings (e.g., IP65) for easy disinfection, and often antimicrobial coatings to prevent pathogen growth.
* Safety: Compliance with medical safety standards like IEC 60601-1 to prevent electrical hazards and ensure patient and operator safety.
* Performance: High resolution, precise color calibration (e.g., DICOM Part 14 for imaging), wide viewing angles, and often fanless designs for quiet, clean operation.
* Durability: Robust construction, industrial-grade components, and resistance to impacts and vibrations for 24/7 operation in demanding settings.
* EMC: Designed to operate without interference from other medical equipment (IEC 60601-1-2 compliant).
Q2: Are medical touch screen displays safe to use in sterile environments like operating rooms?
A2: Yes, absolutely. Medical touch screen displays designed for sterile environments feature specific characteristics that make them safe and suitable. These include:
* IP-rated enclosures: Typically IP65 or higher, meaning they are protected against dust and jets of water, allowing for thorough cleaning with medical-grade disinfectants.
* Flat, seamless surfaces: Reduce areas where bacteria can accumulate, making disinfection more effective.
* Glove-friendly touch technology (often PCap): Allows surgeons and staff to interact with the display without compromising sterility. Always confirm the specific IP rating and cleaning instructions provided by the manufacturer for use in sterile zones.
Q3: Can medical touch screen displays be integrated with existing Electronic Health Record (EHR) systems?
A3: Yes, most modern medical touch screen displays are designed for seamless integration with EHR systems and other hospital information systems (HIS/PACS). They typically offer a range of connectivity options (USB, Ethernet, Wi-Fi) to facilitate data exchange and system access. Many also come as “Medical Panel PCs” or “Medical All-in-One PCs” with integrated computing power specifically for running medical software and accessing EHRs directly.
Q4: What is DICOM Part 14, and why is it important for medical imaging displays?
A4: DICOM (Digital Imaging and Communications in Medicine) is a standard for handling, storing, printing, and transmitting information in medical imaging. DICOM Part 14 specifically defines the “Grayscale Standard Display Function,” which ensures that grayscale images (like X-rays, CT scans, and MRIs) are displayed consistently across different compliant monitors and viewing stations. This consistency is crucial for radiologists and clinicians to accurately interpret diagnostic images, as even subtle variations in brightness or contrast can affect diagnosis. Displays compliant with DICOM Part 14 are factory-calibrated to this standard.
Q5: How do fanless medical touch screens contribute to a better healthcare environment?
A5: Fanless designs offer several significant advantages in healthcare settings:
* Hygiene: Eliminates fans that can draw in and circulate airborne contaminants, dust, and pathogens, contributing to a cleaner environment.
* Noise Reduction: Creates a quieter clinical environment, which is crucial for patient comfort (especially in ICUs) and concentration for medical staff.
* Reliability: Fans are mechanical components prone to failure. Removing them reduces a common point of failure, increasing the overall reliability and lifespan of the device.
* Energy Efficiency: Fanless designs often consume less power.
Latest Content
- Patient Interaction as a System Layer:Why the Bedside Terminal Is the Architectural Core of the Smart Ward
- Designing Workflow-Centered Hospital Systems: Lessons from Real Ward Environments
- Interoperability in Smart Wards:Why Integration Architecture Matters More Than Features
- 7 Powerful Ways Bedside Terminals Are Transforming Modern Hospitals in 2025
- Revolutionizing Patient Care: The Benefits of a Bedside Infotainment Terminal

