Introduction to Medical Displays
Definition of a Medical Display
A medical display is a high-performance monitor specifically engineered for use in healthcare environments. Unlike ordinary consumer monitors, these displays are designed with strict medical standards in mind, offering enhanced clarity, precision, and compliance to ensure accurate interpretation of clinical images.
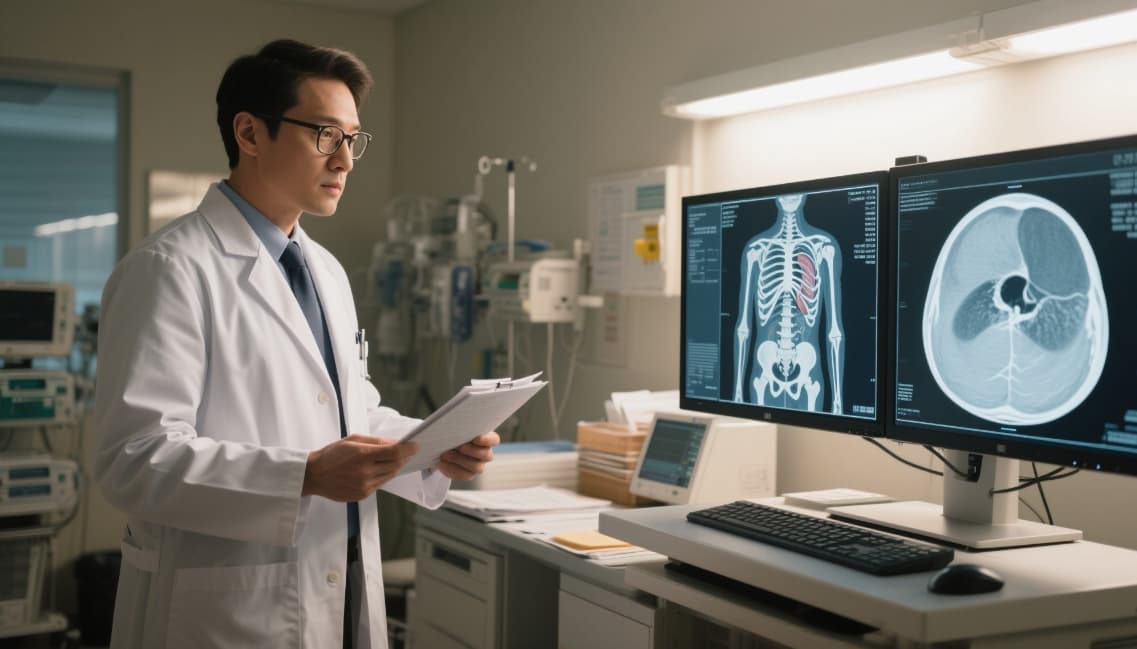
Difference Between Consumer and Medical Displays
At first glance, a medical display might resemble a regular monitor. But under the hood, the differences are massive. Consumer-grade displays aren’t built for the critical demands of clinical environments. They lack color calibration, consistent luminance, and most importantly—DICOM compliance, which is essential for radiology imaging.
Why Standard Monitors Aren’t Enough for Healthcare
In healthcare, every pixel matters. A misinterpreted X-ray or blurry MRI scan could mean a missed diagnosis. Medical displays are made to eliminate that risk, offering clear, calibrated images tailored for tasks like tumor detection, vascular analysis, or pre-surgical planning.
Key Features of a Medical Display
High Resolution and Clarity
Medical images—from MRIs to CT scans—contain fine details that demand ultra-high resolution displays. A pixel-rich screen enables clinicians to zoom in without sacrificing clarity, which is vital for spotting abnormalities.
DICOM Compliance
DICOM (Digital Imaging and Communications in Medicine) is a global standard ensuring that grayscale medical images are displayed consistently across devices. Medical displays undergo DICOM calibration, allowing accurate brightness levels essential for diagnostic integrity.
Brightness and Contrast Ratios
These monitors feature higher brightness levels (often over 1000 cd/m²) and superior contrast ratios to maintain visibility in both brightly lit operating rooms and dim radiology suites.
Color Accuracy for Diagnosis
In pathology, dermatology, or even endoscopy, true-to-life color can be crucial. Medical displays use 10-bit or higher color depth, enabling more accurate and consistent color representation compared to typical 8-bit consumer monitors.
Anti-Glare and Cleanable Surfaces
To meet hygiene standards, most medical displays come with anti-reflective coatings and easy-to-clean surfaces that can withstand harsh disinfectants—perfect for operating rooms and ICU setups.
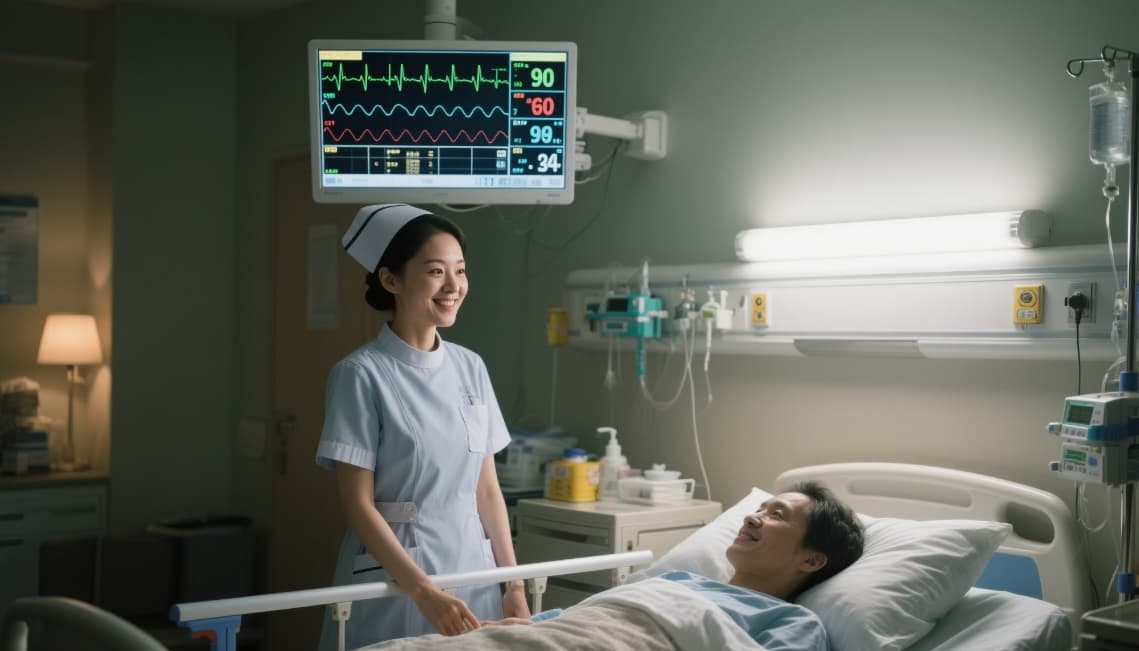

Types of Medical Displays
Diagnostic Displays
These are high-resolution grayscale monitors used in radiology and mammography. They support precise readings of X-rays, MRIs, and CT scans with pinpoint accuracy.
Surgical Displays
Surgical monitors are larger, often mounted in ORs, and provide 4K or higher resolution with waterproof and sterile-friendly designs. They display real-time surgical camera feeds or live imaging.
Clinical Review Monitors
These are used for non-diagnostic tasks like reviewing patient data or displaying images during rounds. While they meet medical safety standards, they’re more affordable and less feature-rich.
Patient Bedside Monitors
Compact and durable, these displays show real-time vitals, waveforms, and EHR info at the patient’s bedside. They’re built for 24/7 operation with minimal power consumption.
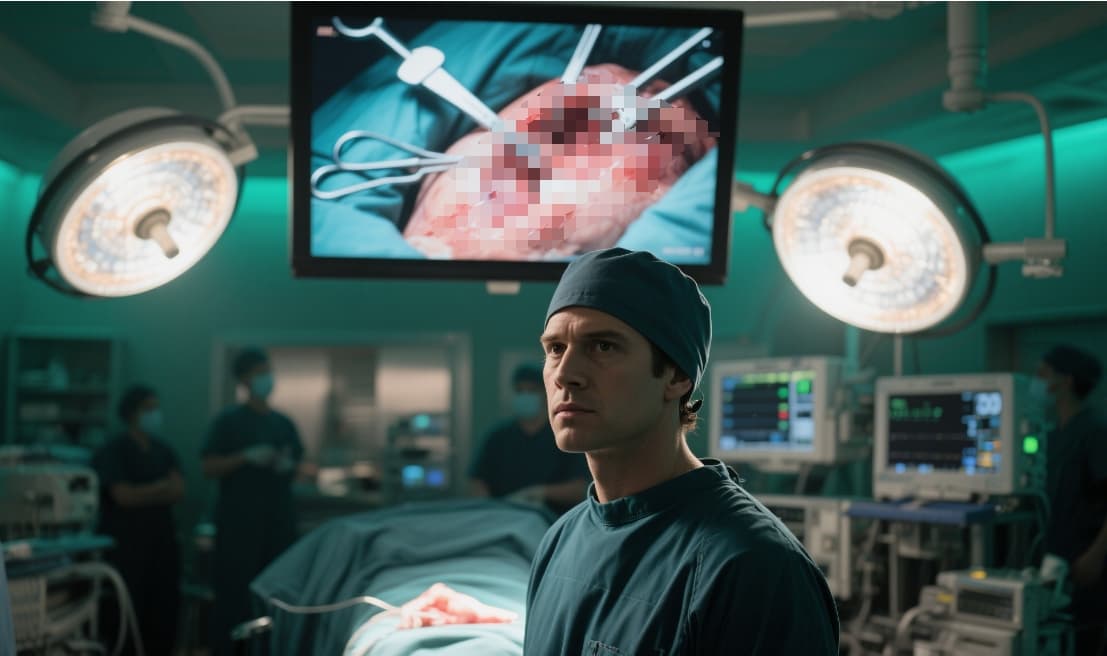
Applications in the Medical Field
Radiology
Here, image fidelity is king. Radiologists depend on high-resolution DICOM-compliant displays to examine X-rays, MRIs, and other imaging modalities in the most minute detail.
Surgery
During operations, especially minimally invasive procedures, real-time visuals from laparoscopes and endoscopes are displayed on surgical monitors. Color accuracy and lag-free performance are critical.
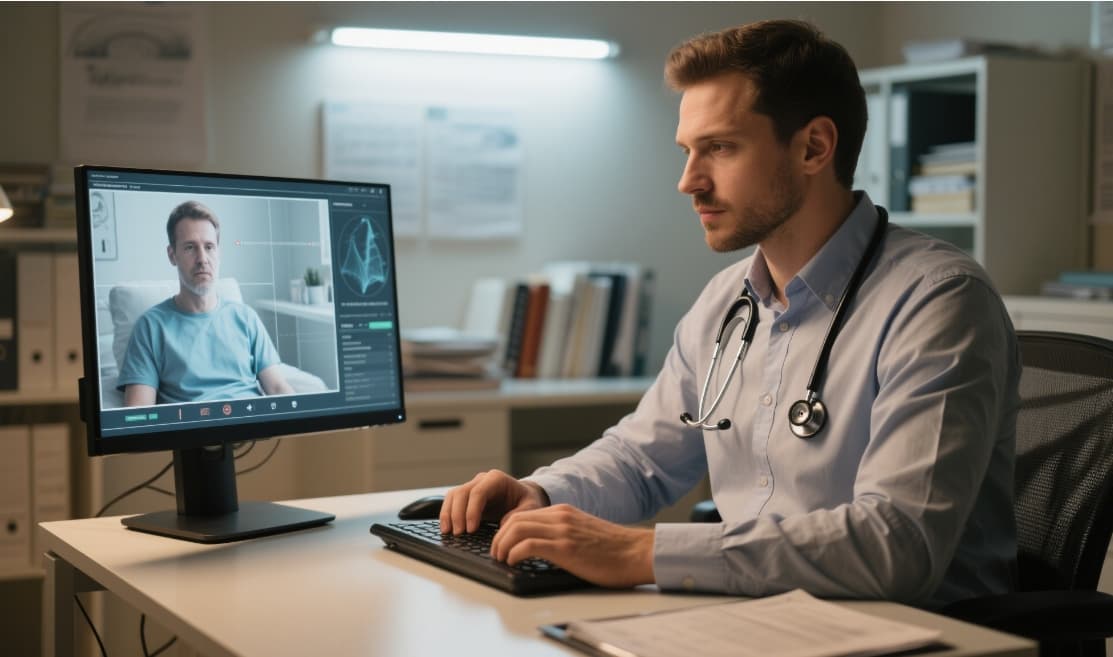
Telemedicine
In the world of virtual care, medical displays help bridge the distance. High-quality video displays allow doctors to assess wounds, skin issues, or physical conditions remotely, without losing visual fidelity.
Patient Monitoring
Vital signs must be clear and unambiguous. Bedside monitors with robust displays ensure that clinicians can act immediately when abnormalities appear.
Importance of Medical-Grade Certification
FDA and CE Compliance
Medical displays must comply with strict international standards, including FDA approval in the U.S. and CE marking in Europe, ensuring safety and performance.
IEC 60601 Certification
This ensures the display is safe for use in medical environments with electromagnetic interference control, isolation from power surges, and durable enclosures.
How Medical Displays Improve Patient Outcomes
Better Diagnostic Accuracy
With sharper images and proper calibration, misdiagnoses drop and early detection becomes more feasible, directly impacting patient survival rates.
Enhanced Visualization in Surgery
Clear, real-time imaging during procedures improves surgical precision, reduces risks, and shortens recovery time.
Reliable Telehealth Communication
In remote consultations, crisp visuals reduce guesswork, allowing doctors to make informed decisions faster.
Challenges in Implementing Medical Displays
Cost and Budget Constraints
Let’s face it—these monitors aren’t cheap. High upfront costs can make them inaccessible for smaller clinics, although the long-term ROI often justifies the expense.
Compatibility with Existing Systems
Medical displays must integrate with PACS, RIS, HIS, and more. Poor compatibility can disrupt workflows, so interoperability is crucial.
Future Trends in Medical Displays
4K and 8K Technologies
As imaging techniques evolve, so must displays. Ultra-HD resolutions are becoming the norm in surgical and radiological applications.
AI-Powered Imaging Integration
Displays are being developed with AI tools that help flag anomalies or assist in real-time diagnostics, saving time and reducing human error.
Wireless and Portable Displays
Wireless, battery-operated displays are gaining traction, offering mobility and flexibility, especially for emergency care or rural clinics.

Conclusion
So, what is a medical display? It’s not just another screen—it’s a precision tool at the heart of modern medicine. Whether you’re diagnosing a tumor, monitoring vitals, or performing surgery, a medical display ensures that what you see is accurate, timely, and actionable. These specialized monitors support faster decisions, better outcomes, and ultimately, healthcare that patients can trust.
FAQs
1. What is DICOM, and why is it important?
DICOM is a medical standard that ensures consistent grayscale and brightness in imaging across devices. It’s vital for diagnostic accuracy, especially in radiology.
2. Can I use a medical display as a regular computer monitor?
Technically yes, but it’s overkill. Medical displays are built for clinical precision, which most home or office users don’t need—and they come at a higher cost.
3. How long do medical displays last?
High-quality medical monitors can last 5 to 10 years, depending on usage, environment, and maintenance.
4. Are there portable medical displays?
Yes, newer models are designed to be compact, wireless, and battery-powered, making them suitable for mobile clinics or field hospitals.
5. What makes a display suitable for operating rooms?
OR monitors must be sterile-safe, waterproof, ultra-bright, and high-resolution, often with touchscreen functionality and real-time imaging capability.
Latest Content
- Identity & Security at the Bedside:Building Trust in Smart Ward Architectures
- Preparing Smart Wards for Hybrid Care and Long-Term Scalability
- Patient Interaction as a System Layer:Why the Bedside Terminal Is the Architectural Core of the Smart Ward
- How to Use a Bedside Infotainment Terminal Effectively
- Revolutionizing Patient Care: The Benefits of a Bedside Infotainment Terminal